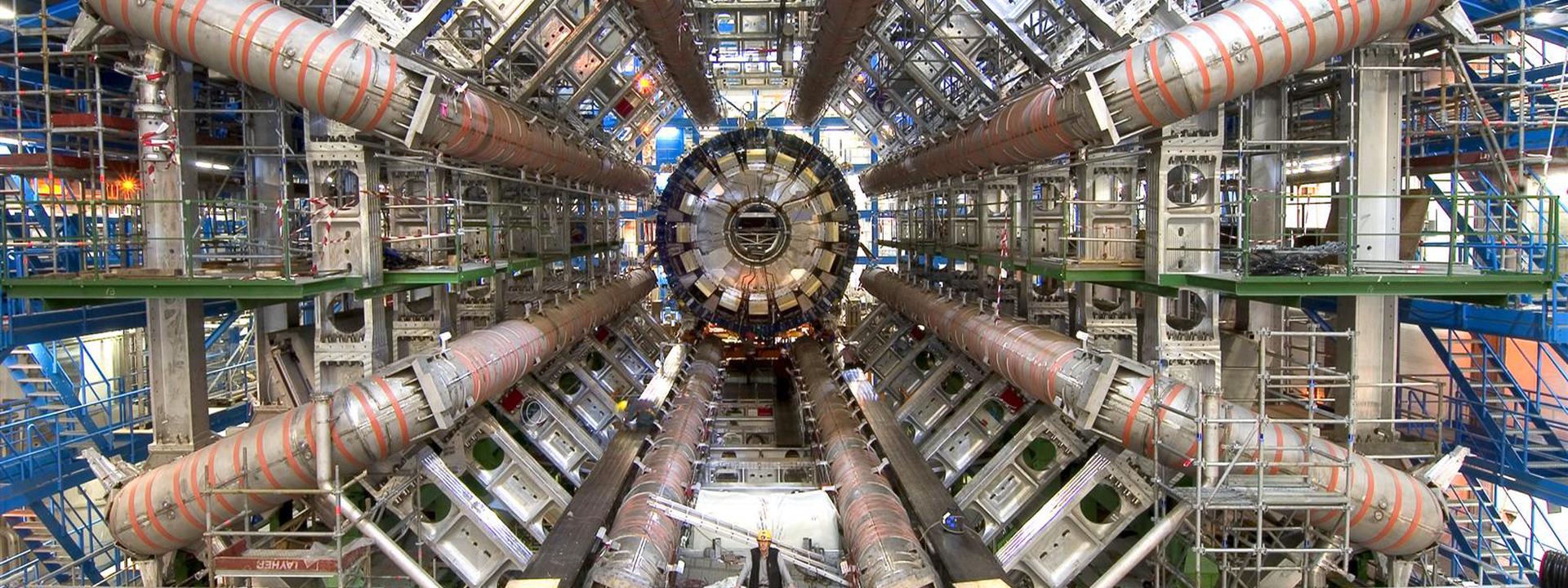
CERN’s Large Hadron Collider (LHC) delivered the first high-energy proton-proton collisions in 2010, opening a new energy frontier in particle physics. ATLAS is one of the four large detectors at the LHC involving about 3000 scientists. With a 25-year involvement in the ATLAS experiment, IFAE has strongly contributed to a broad spectrum of topics critical to the scientific exploitation of the experiment
The Collider Physics group at IFAE is led by M. Bosman.
The ATLAS Tile Hadronic Calorimeter (TileCal)
IFAE played a central role in the design, construction and commissioning of the Tile hadronic Calorimeter (TileCal), finished in 2009. Since 2010, IFAE strongly contributes to various aspects of the TileCal operation, data reconstruction, calibration, data quality monitoring, and luminosity measurement. IFAE researchers often act as TileCal run coordinators. During the last years the group has led the R&D for the new structure hosting the upgraded front-end electronics, needed for the high luminosity LHC (HL-LHC) period starting in 2027. The production of the new structures started in 2019 and is expected to last 3 years.
The ATLAS Trigger and Data Aquisistion (TDAQ)
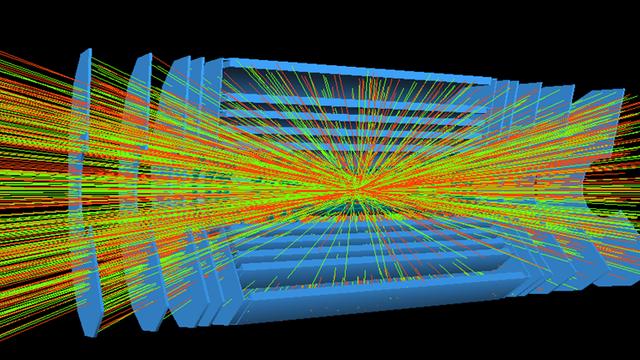
IFAE has contributed to the development and operation of the data acquisition and event selection system (trigger), critical for an efficient selection of the most interesting collisions. IFAE was one of three groups developing the software infrastructure of the high-level trigger and held several coordinating responsibilities within the ATLAS trigger group. IFAE also played a key role in developing the algorithms for the selection of events with tau leptons, later extended to jet triggers. In order to cope with the higher luminosity of Run 2 (2015-2018), ATLAS installed a new processor to perform real-time event selection based on topological variables. IFAE made major contributions to the simulation of the processor, its commissioning and validation with data. Moreover, IFAE contributed to the operations of the whole trigger system with the overall coordination of the trigger menu. The trigger work at IFAE will continue in preparation for the new Run 3 scheduled for spring 2022.
Physics Analysis Program
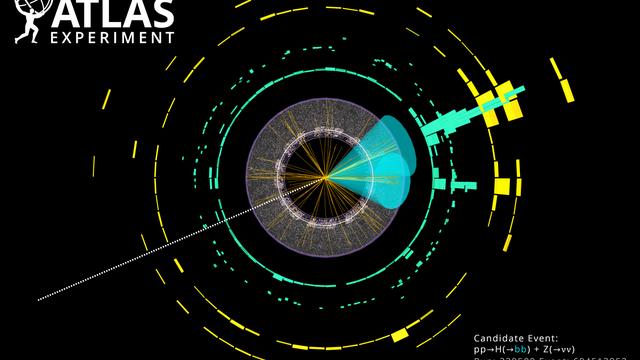
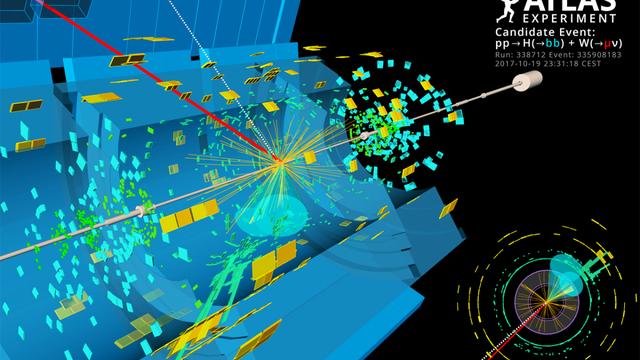
The institute deployed a strong and rich physics analysis program at the LHC, expanding from precise Standard Model background measurements to Higgs boson physics. During Run 2, when LHC collided protons at a center-of-mass energy of 13 TeV, IFAE developed a broad program of searches for new phenomena, including dark matter, invisible Higgs boson decays, supersymmetry, compositeness, new heavy Higgs bosons, as well as precise measurements of the interactions between the top and bottom quarks and the Higgs boson. IFAE, which represents about 1% of ATLAS, directly contributes to about 10% of ATLAS publications. IFAE researches have held a number of physics-related coordination positions. Most notably, A. Juste is the current co-coordinator of the ATLAS Exotics Physics Working Group.
Data processing of the LHC data
IFAE is a main actor in the data processing of the LHC data. In 2003, IFAE and CIEMAT founded the Port d’Informació Científica (PIC), one of 13 LHC Tier-1 data centers in the world and the only one in Spain. As such, PIC participates in the overall effort of processing and distributing the tens of PB of data the LHC produces every year. Year after year, PIC, which operates 24/7, is listed in the top three of Tier-1 centers in terms of reliability.

3D silicon pixel sensors for ATLAS
IFAE in collaboration with the CNM center in the UAB campus led the development of the ultra-radiation-hard 3D silicon pixel sensors for ATLAS. The institute made key contributions to the current detector systems based on this technology: providing 3D sensors for the innermost pixel layer (IBL) in 2014 and constructing in 2016 the first stations for the ATLAS Forward Protons (AFP) tracking system, finished in 2020. Recently, the design of the 3D sensors has been adapted to satisfy the HL-LHC requirements, and the technology has been selected for the innermost layer of the new ATLAS tracking system. IFAE is now preparing to produce the pixel modules and deliver them to CERN in the mid 2020s. This is arguably the most demanding piece of instrumentation of ATLAS: a 250-um-thick silicon sensor that will reside 3cm away from the interaction point and that has to provide excellent position resolution during many years of LHC operation in a high radiation environment.
High Granularity Timing Detector (HGTD)
IFAE has been deeply involved in the R&D effort to design and fabricate a timing detector to mitigate the effect of pile-up at the HL-LHC. Using timing, one can identify the origin of the reconstructed tracks, thus reducing the effect of overlapping collisions. IFAE proposed the Low Gain Avalanche Detector (LGAD) technology developed at CNM to be used in a High Granularity Timing Detector (HGTD), demonstrating that LGAD sensors can provide the needed time resolution in the presence of the expected large radiation doses. After its adoption by ATLAS, IFAE is now working on the corresponding ASIC design and has developed the hybridization process for the HGTD.
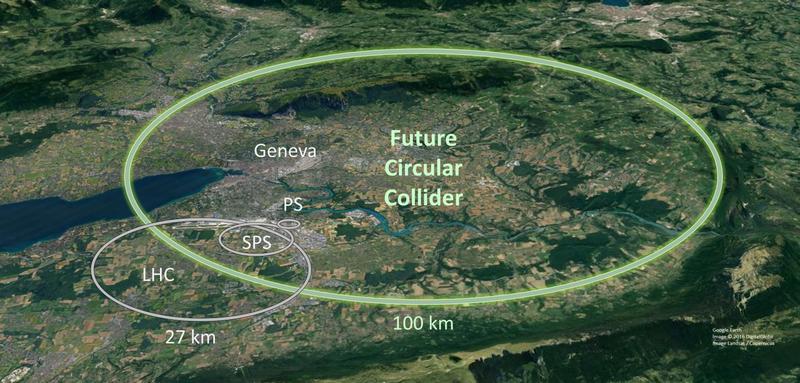
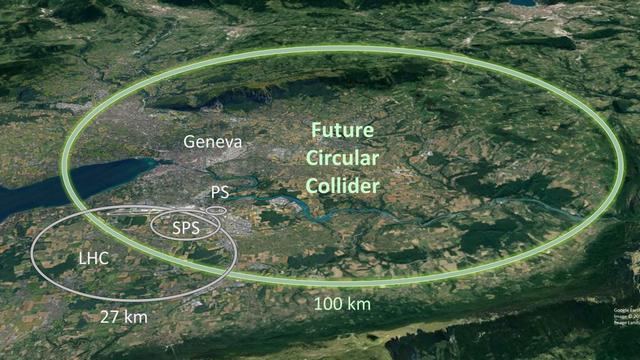
High temperature superconductor coated conductors for the Future Circular Collider (FCC-hh)
A collaboration between CERN and Spanish centers ICMAB, UPC, ALBA and IFAE was established in 2016 to evaluate high temperature superconductor coated conductors (HTS-CC) as candidates for the beam screens of the Future Circular Collider (FCC-hh). To study its properties under mechanical stress, IFAE designed and built a dedicated machine that holds a large sample of powered HTS-CC, applies mechanical stress to it, and measures the distributions of mechanical deformation and current density over its surface. The work was funded by CERN for three years (2016-19), was very positively reviewed, and has been recently extended to build a proof-of-concept FCC-hh beam screen device based on HTS-CC.